主流派=チョムスキーとその「仲間」たち
(16) a. # Colorless green ideas sleep furiously.
b. *Ignored idea my was.
(17) a. 私、電話する、あなたに、明日。
b. 私は明日あなたに電話します。
===> autonomy of syntax
(Transformational) Generative Grammar (変形)生成文法
(理論)言語学の目標:
注意:単にチョムスキーやその仲間たちの興味の対象が
syntax であり、文脈等でないということにすぎない。
心理学的、計算主義 ==> 認知科学 (Cognitive Science)
cf. 河合塾(編)『学問の鉄人:大学教授ランキング文科系編』(別冊宝島)
4.1 1957-1980
4.1.1 Phrase Structure Rules

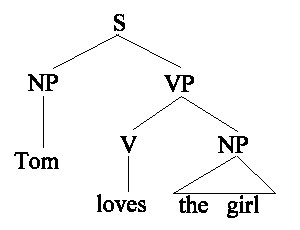
(18) a. S → NP VP
b. VP → V NP
deep structure (深層構造)
↓
surface structure(表層構造)→ 音声解釈(音韻論)
要するに、
Ken kicked Mary.
↓
Mary was kicked by Ken.
または、
I wonder ___ Ken met who yesterday.
↓
I wonder who Ken met ___ yesterday.
など。4.2 1980年代
pro-drop: 主語が省略出来るかどうか
No: English, etc.
Yes: Spanish, Italian, etc.
(19) *Who do you think that t left.
(19) は英語では駄目だが、Spanish/Italian では OK。
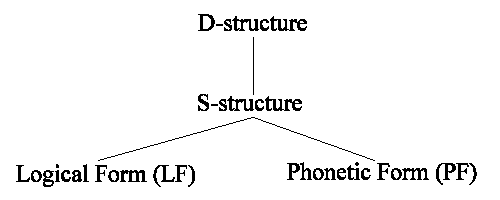
4.3 1990年代
Minimalist Program: 「あるのは LF と PF だけだ」(以下、省略)
4.4 VP
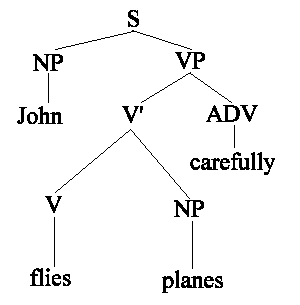 VP がある、すなわち、主語は仲間外れ。
VP がある、すなわち、主語は仲間外れ。
VP constituent の証拠:
pause:
(21) Ken | likes Mary.
pseudo-cleft:
(22) a. Bill put [NP Marcia's neckless] [PP in the safe].
b. What Bill put ___ in the safe was Marcia's necklace.
c. *What Bill put ___ the safe was Marcia's necklace in.
What ... ___ ... is/was X: X は constituent
(23) What Roger did ___ was find the correct analysis.
VP fronting/preposing/movement:
(24) a. Bill said he would buy a motorcycle, and buy a motorcycle he did.
b. *Bill said he would buy a motorcycle, and buy did he a motorcyle.
(McCawley 1988: 184)
anaphora:
(25) do, do it, etc.
VP ellipsis/deletion:
(26) a. You may play the guitar if you want to ___.
b. Yes, I can ___.
BTW, no contraction in (26a-b).
5. 心理的実在物としての文法
5.1 Psychological Reality of VP
本当に VP constituent は native speaker の頭の中にあるのか?
(27) That he was happy was evident from the way he smiled.
* * * * * * ** *
このうちのどれか1つにクリック音が入っている文をきかせると、
happy と was との間にクリック音が入って
いる時が最も正答率が高い。
息つぎが入っているからでは?
==> そうではない。
(28) As a result of their invention's influence | the company was given an award.
* *
(29) The chairwoman whose methods still influence the company | was given an award.
* *
被験者は、息つぎが縦線のところに入っていると言う。
(28)-(29) の下線部を入れ替えて聞かせる。しかし、息つぎの場所について の被験者の判断は同じだし、またクリック音にしても、縦線のところでき きとられる傾向。
5.2 Morphological Rules
Jean Berko の実験 (1958)。
(30) a. Here's a man who knows how to rick. He did the same thing yesterday.
He....
b. ricked.
(Pinker 1995a: 117)
(31) a. This is a wug. (accompanied by a picture of an
imaginary birdlike animal)
b. There are two of them. (accompanied by a picture of
two of the imaginary animal)
c. There are two ___
d. wugs.
(Akmajian et al., p. 468)
5.3 First Language Acquisition チョムスキーの理論の基礎:統語論の数学的性質
プログラミング言語 --> (compile) --> バイナリ
言語習得: (A)経験+(B)一般的知能+先天的知識etc.=文法
Learnability Theory (a branch of theoretical computer science;
Pinker 1995b).
一般的知能と言語能力は異なっている(失語症研究など; Pinker 1995a)。
overregularization (Pinker 1995a)
(32) (I) go, went --> (II) goed, wented --> (III) go, went
| Bahaviourism(行動主義) | 刺激-習慣強化 |
| Chomsky | 言語は innate (生得) |
表現を変えれば、人間の脳が、UG に合うような言語しか習得出来ない
構造になっているということ。
phoneme contrast (のみ)をききわける infants (Pinker 1994, Werker 1995, etc.)
cf. 日本人の子供は、6〜8ヶ月時には /la/ と /ra/ の聞き分けが
出来るが、10〜12ヶ月時には出来なくなっている (Werker 1995:
92)。しかし、単に耳が悪くなるという話ではなく、母語の音韻
論の干渉 (ibid: 96)。
Poverty of Stimulus (Chomsky) 5.3.1 英語
(33) a. John saw Mary with her best friends's husband.
b. Who did John see Mary with ___?
c. John saw Mary and her best friends's husband.
d. *Who did John see Mary and ___?
(34) a. John liked the pictures of Bill that Mary took.
b. John liked Mary's pictures of Bill.
c. John liked the pictures of himself that Mary took.
d. *John liked Mary's pictures of himself.
a--b からそれぞれ wh 構文の規則や所有形の規則を学んだなら、
c から d を作りそうなものなのに、実際には子供は作らない。
なぜか? ( d が駄目だということは、チョムスキーたちの研究
までは、気づかれていなかった)
親は、意味さえ通じれば、普通統語論的な間違いを直さない。
(35) Child: Mama isn't boy, he a girl.
Mother: That's right.
(36) Child: And Walt Disney comes on Tuesday.
Mother: No, he does not.
またそもそも、話せないけれど、聞いて文法性の判断をきちんと出来る
子供もいる (Pinker 1995a: 113, 1995b: 154)。
但し、不規則動詞の現在形・過去形という arbitrary pairing を記
憶に貯え、かつそれを呼び出せるようになるためには、何度も不規
則形を聞く必要がある。
===>
不規則動詞が規則動詞に変わって行く歴史的傾向:頻度が低いもの
ほど規則化しやすい。
以下、英語ではなく American Sign Language (ASL) および
{\sl creole\/} について考える。(Gleitman and Newport 1995)
5.3.2 ASL
ASL を0才から習得したグループを A、4〜6才に習得した グループを B、12才から習得したグループを C とする。50才以上の 時に調べると、B-C グループでは function morpheme や complex sentence がダメ。
deaf 同士で育てる(sign language の input なし)。すると、 sign language を invent。習得の過程は hearing child と同じ。 但し、function morpheme (article, auxiliary) や bound morpheme (tense, case) は出て来ない。
5.3.3 Pidgin and Creole
Pidgin: mixture of several languages by adults
Creole: acquired by native speakers
pidgin には function morphome や complex sentence がないが、
creole には出てくる。
5.4 Second Language Acquisition and Teaching
行動主義 --> pattern practice
チョムスキー --> 文法中心
===>
Natural Approach (Kraschen and Terrell 1988)